Expert in Camera Module Solution

Expert in Camera Module Solution
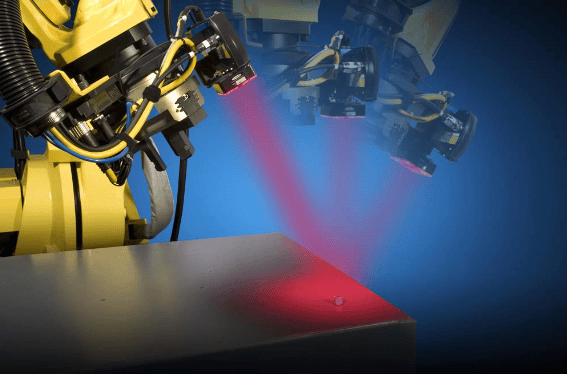
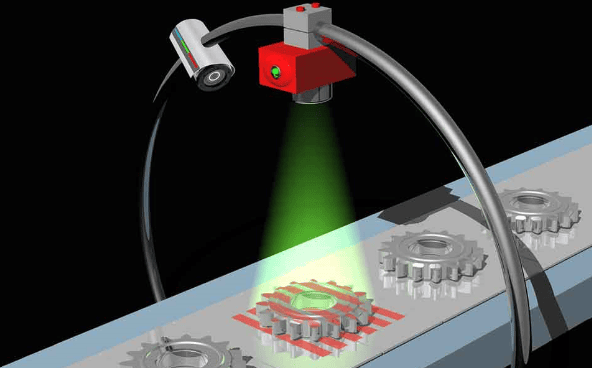
Machine vision is the technology and methods used to provide imaging-based automatic inspection and analysis for such applications as automatic inspection, process control, and robot guidance, usually in industry. Machine vision is a term encompassing a large number of technologies, software and hardware products, integrated systems, actions, methods and expertise. Machine vision as a systems engineering discipline can be considered distinct from computer vision, a form of computer science. It attempts to integrate existing technologies in new ways and apply them to solve real world problems. The term is the prevalent one for these functions in industrial automation environments but is also used for these functions in other environments such as security and vehicle guidance. (From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia)
In short, machine vision is the ability of a computer to see; it employs one or more video cameras, analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) and digital signal processing (DSP). The resulting data goes to a computer or robot controller. Machine vision is similar in complexity to voice recognition.

Two important specifications in any vision system are the sensitivity and the resolution. Sensitivity is the ability of a machine to see in dim light, or to detect weak impulses at invisible wavelengths. Resolution is the extent to which a machine can differentiate between objects. In general, the better the resolution, the more confined the field of vision. Sensitivity and resolution are interdependent. All other factors held constant, increasing the sensitivity reduces the resolution, and improving the resolution reduces the sensitivity.
Human eyes are sensitive to electromagnetic wavelength s ranging from 390 to 770 nanometers (nm). Video cameras can be sensitive to a range of wavelengths much wider than this. Some machine-vision systems function at infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV), or X-ray wavelengths.
Binocular (stereo) machine vision requires a computer with an advanced processor. In addition, high-resolution cameras, a large amount of random access memory (RAM), and artificial intelligence (AI) programming are required for depth perception.
Machine vision is used in various industrial and medical applications. Examples include:
-Electronic component analysis
-Signature identification
-Optical character recognition
-Handwriting recognition
-Object recognition
-Pattern recognition
-Materials inspection
-Currency inspection
-Medical image analysis
The term machine vision is often associated with industrial applications of a computer's ability to see, while the term computer vision is often used to describe any type of technology in which a computer is tasked with digitizing an image, processing the data it contains and taking some kind of action.
Author: Margaret Rouse
Margaret Rouse writes for and manages WhatIs.com, TechTarget’s IT encyclopedia and learning center. She is responsible for building content that helps IT professionals learn to speak each other’s highly specialized languages.